What’s selective photothermolysis?
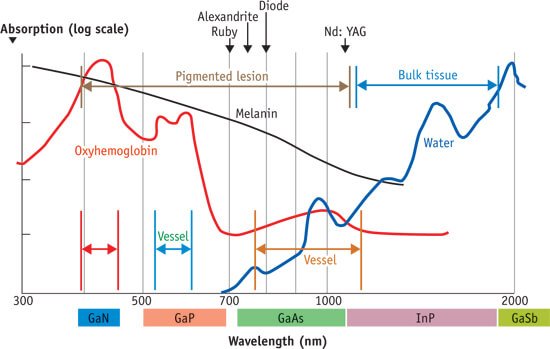
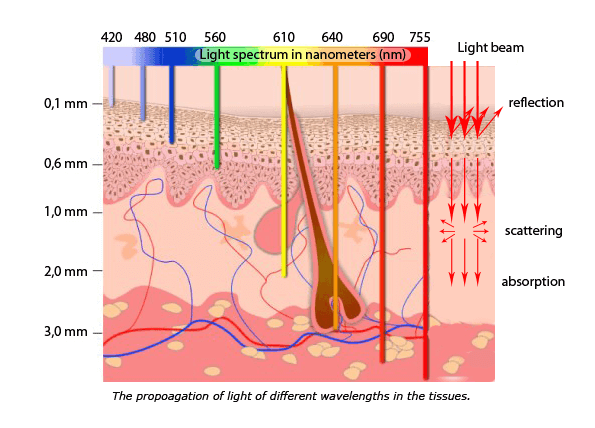
Selective photothermolysis (Part 2) Melanin absorbs across a wide spectrum of wave-lengths. Eumelanin, the primary chromophore in the epi-dermis and darkly pigmented hair follicles, has a broad absorption spectrum spanning from ultraviolet light to the near-infrared region. Eumelanin is the chromophore targeted in lentigo simplex. It is also the target in laser hair removal with…